
Energy and water development corp.
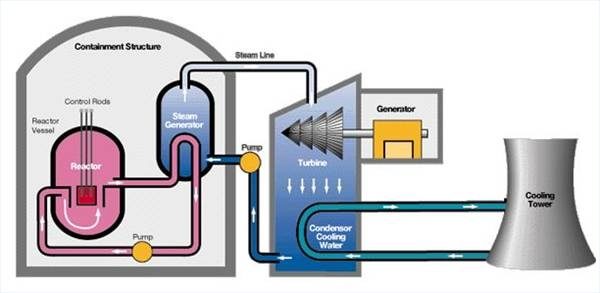
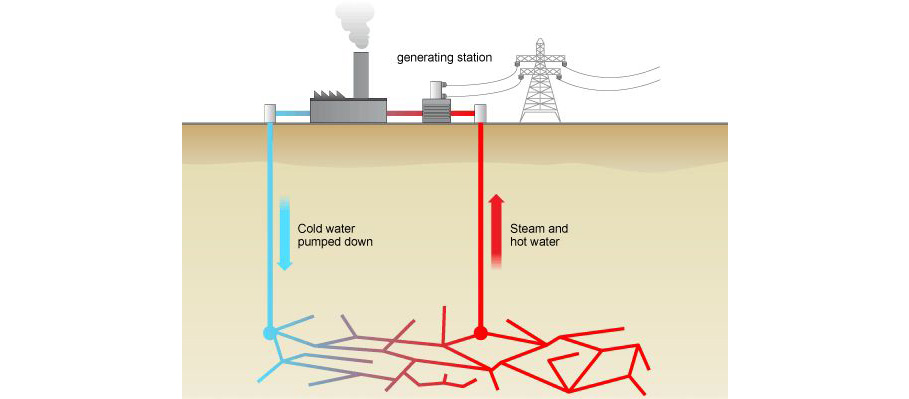
Steam Generator Energy from steam
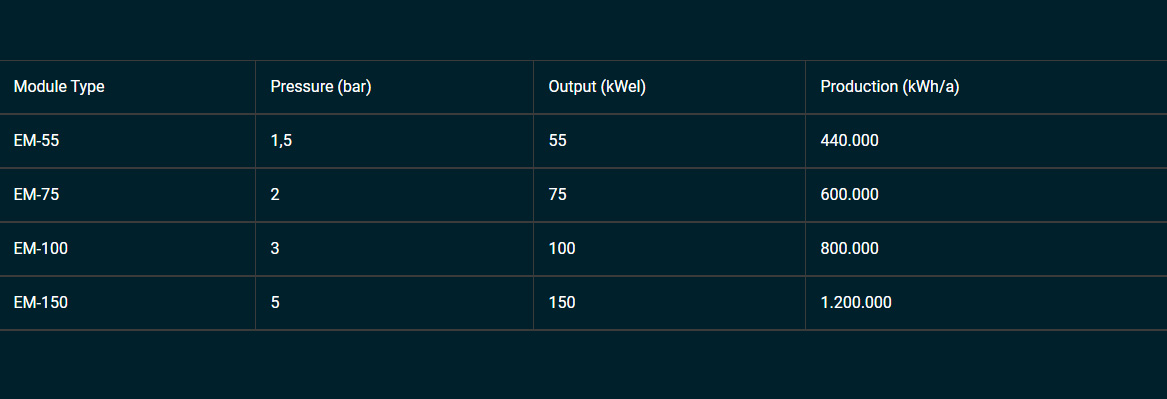
The Energy Module turns low pressure steam of 0.6 to 5 bars usually an industrial waste product into electrical energy. With zero CO2 emissions.
No additional energy resources are required. Not a single ounce of gas or coal or oil, no wind turbine and no solar system is needed to operate the Energy Module.
Climate change and global development in this century increased energy demand and prices.
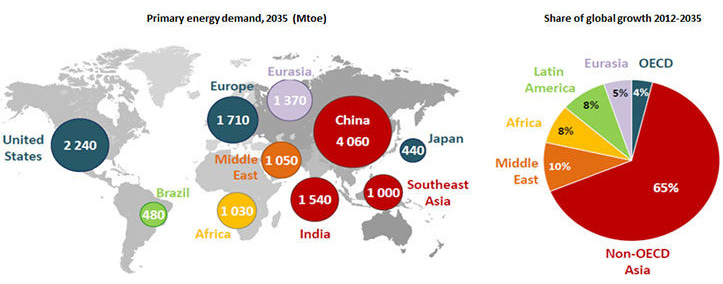
Total Electricity Consumption
Total CO2 Emissions from Fuel Combustion
All loose industrial steam on the air is electricity lost
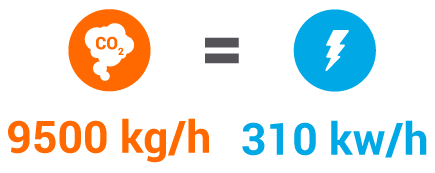
Electricity prices in leading economies worldwide
Electricity prices in leading economies worldwide
Total Electricity
Consumption
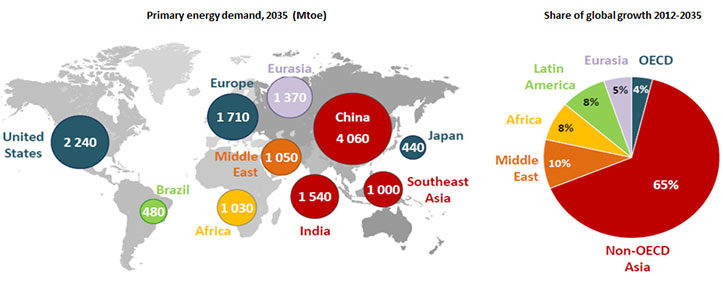
In 2018, world total electricity final consumption reached 22 315 TWh, 4.0% higher than 2017. In 2018, OECD total electricity final consumption was 9 728 TWh, 1.8% higher than in 2017, while final electricity consumption in non-OECD countries was 12 587 TWh, an increase of 5.7% from 2017.
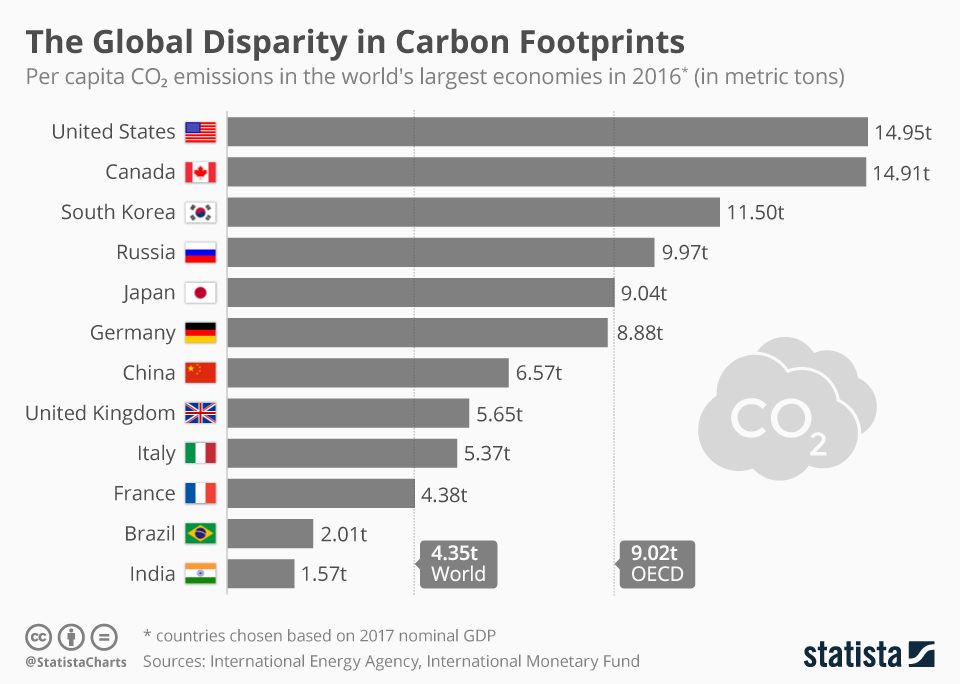
Total CO2 Emissions from
Fuel Combustion
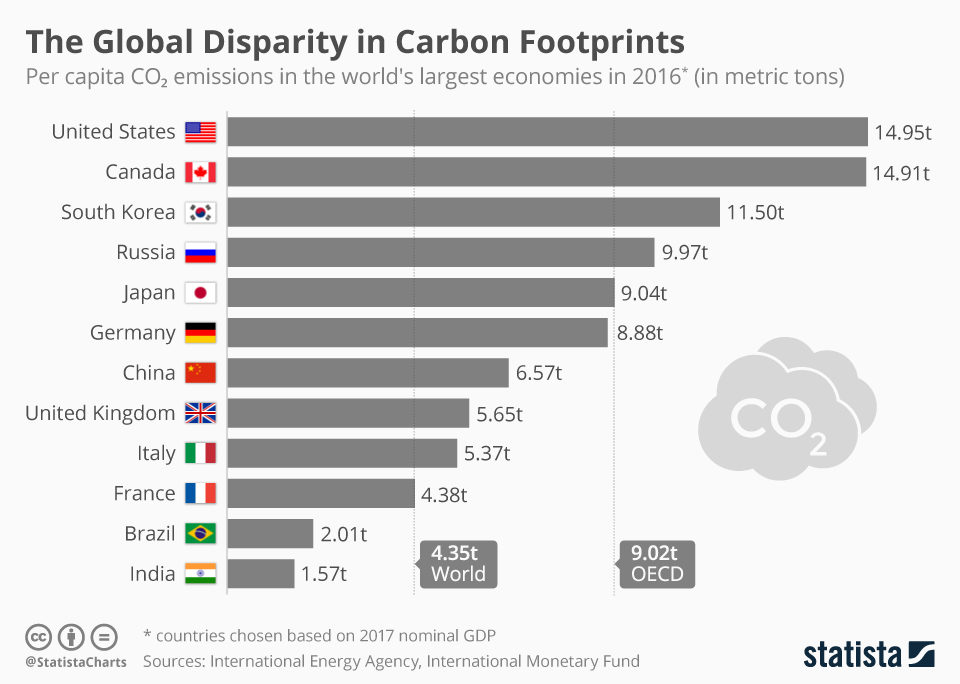
Global CO2 emissions from fuel combustion reached a historical high of 33.5 GtCO2 in 2018 driven by a robust growth in population and economic activity
All loose industrial steam on the air is
Electricity lost
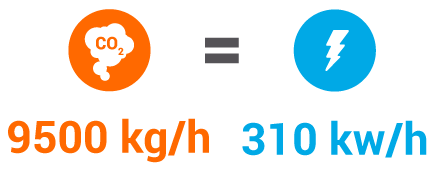
The increasingly use of renewable energy sources (RES) significantly contributes to the reduction of CO2 emission and to the sustainability of the overall energy system.
Steam Generator Markets
Steam Generator Benefits
- Food Industry
- Cooling water in block heat-and-power plants
- Processed water in the chemicals industry
- Block heat-and-power plant operators
- Steelworks
- Aluminium smelters
- Solar thermic
- Saving fossil fuels
- Environmental aspect
- Using your own, self-made and clean energy
- Reducing costs for procuring (fossil) energy
- Feeding the produced energy into a public grid
- Quick amortization of procurement costs
- Reducing CO2 emissions
- Certificates for emissions trading
Steam Generator Markets
The waste heat given off in industrial processes in the low-temperature range up to 100°C constitutes an energy potential in all industrialized countries that is left largely untapped. EAWD offers a unique process for generating an electric current from low-temperature heat, thus enabling the potential from the heat produced as a discarded by-product of many industrial processes to be made use of.
In addition to this, the process can also be applied to generate electricity by utilizing the heat from other sources, including: solar energy; geothermal heat; technically conditioned waste heat flows from power stations; and, combined heat-and-power (CHP) plants.

Through the specific utilization of low-temperature heat for the generation of electricity, a major worldwide contribution could be made to reducing the consumption of fossil energy resources and cutting down on CO2emissions.
The system can be applied, for instance, by utilizing the waste heat from liquid media at temperatures above 70°C.
The unique breakthrough that the energy modul has achieved is to make use of existing, but up to now completely neglected resources to produce electrical energy. With the Energy Module, low-pressure steam that to-date was considered as a waste product deriving from a range of industrial processes, is transformed into electrical energy – a significant step forward in zero-carbon power generation, having both economic and environmental benefits.
Top 5 CO2 emissions:
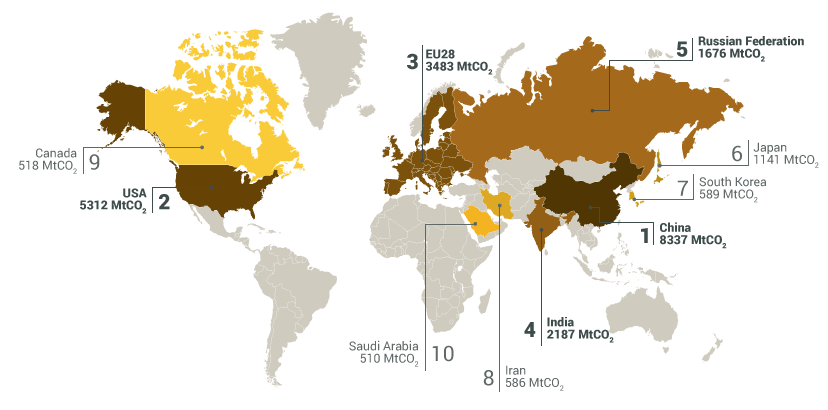
1. China: 8,337 MTCO2
2. USA: 5,312 MTCO2
3. EU28: 3,483 MTCO2
4. India: 2,187 MTCO2
5. Russia: 1,676 MTCO2





